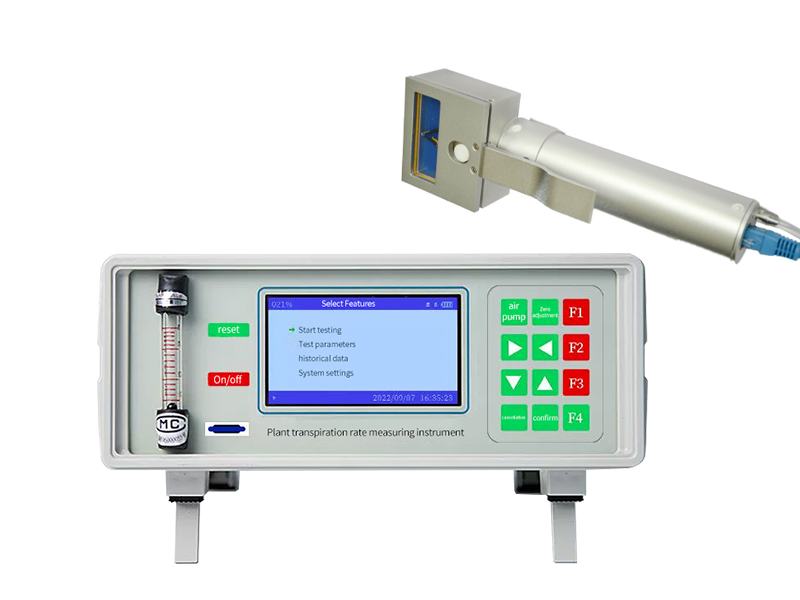
Overview:
Plant steaming rate refers to the speed that is emitted into the atmosphere in the atmosphere when moisture passes through the plant in the plant through the plant. The steaming effect of plants can produce steaming and tension. Steaming tension is the main driving force for plant passive water absorption and transfer of moisture, which is especially important for tall trees; steaming effects can promote the transportation of material transportation in the juice of the wood, mineral salt and root systems in the soil. The synthetic substances can be transported and distributed to all parts of the plant with the absorption and flow of water; the steaming effect can also reduce the temperature of the plant and prevent the leaves from being burned. During the steaming process, a large amount of radiation can be dispelled. The normal development of the steaming effect is conducive to the assimilation of CO2. This is because when the blades are transparent, the pores are open, and the open air holes become a channel for CO2 to enter the blade. Therefore, the crop plant steaming rate measuring meter is of great significance for agricultural research, teaching, gardening research, and forestry research.
Test indicators:
Leaf temperature
Photosyal effective radiation (PAR)
Air temperature
Air humidity
Steaming rate
Pore
Pore impedance
Technical indicator:
Air temperature:
Swiss imported high-precision digital temperature sensor, measurement range: -20-80 ° C, resolution: 0.1 ° C, error ± 0.2 ℃
Leaf temperature:
Platinum resistance, measurement range: -20-60 ℃, resolution: 0.1 ℃, error ± 0.2 ℃
humidity:
Swiss imported high-precision digital humidity sensor, measurement range of 0-100%, resolution: 0.1%, error ≤ ± 3%
Photosyal effective radiation (PAR):
Silicon-optical battery with a modified filter, measurement range: 0-3000? Molm ㎡/second, accuracy <5? Molm ㎡/second
Flow: Micro flow meter, the flow is set in any set of 0-1.5L, and the airflow is stable. Error: 1%, <± 0.2%in the range of 0.2 ~ 1L/ min
Leaf room size: standard size 55 × 20mm, can be customized according to customer needs
Working environment: temperature 20 ° C-50 ° C, relative humidity: 0-100%(no water vapor condensation)
Power: Large -capacity DC8.4V charging lithium battery can work continuously for 20 hours at a time. (Different external light sources)
Data storage: memory 16g, extension to 32G
Data transmission: USB connection computer can directly export data.
Display: 3.5 "TFT real color LCD screen color display, resolution 800 × 480, clearly visible in strong light
Volume: 260 × 260 × 130mm
Weight: Host 3.25kg;
Factors affecting the steaming effect
1. Internal factors that affect the steaming effect
(1) Stomatal Frequency (Stomatal Frequency, which is the number of air holes on each square millimeter).
(2) The diameter of the pores of the pores is large, the internal resistance is small, and the steaming is fast.
(3) The lower cavity volume of the cavity of the cavity under the pores is large, and the vapor pressure difference between the inside and outside of the leaf, and the steam is fast.
(4) The openness of the pores is large, and the steam is fast; the other is slow.
2. External factors affecting the transpiration effect depends on the size of the vapor pressure difference and diffusion resistance in the inside and outside of the leaf. Therefore, any external factors affecting the variables and diffusion resistance of the inside and outside of the leaf will affect the rate of steam.
(1) The impact of light light on the steaming effect is first to cause the openness of the pores, reduce the resistance of the pores, and thereby enhancing the steaming effect. Secondly, light can increase the temperature of the atmosphere and leaves, increase the pressure difference between inside and outside the leaves, and speed up the rate of steam.
(2) Temperature and temperature have a great impact on the rate of steaming. When the atmospheric temperature rises, the leaf temperature is 2 to 10 ° C higher than that of the air temperature, so the increase in the voltage pressure of the lower cavity of the pores is greater than the increase of the air vapor pressure, which increases the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the leaves and increases the speed of the steam. When it is high, the leaves are overwhelmed, the pores are closed, and the steam is weakened.
(3) When the humidity is the same, the greater the relative humidity of the atmosphere, the larger the steam pressure, the smaller the pressure difference between the inside and outside of the leaves, and the water vapor in the cavity of the cavity of the cavity of the pores is not easy to spread, and the steam is weakened. If the humidity is low, the rate of steaming is accelerated.
(4) The wind speed and wind speed are large, which can spread the diffusion layer of the water vapor of the outer pores of the leaf surface, and the air with a relatively low humidity can not only reduce the diffusion resistance, but also increase the variable pressure difference between the inside and outside of the leaf. Essence Strong winds may cause air holes to be closed, internal resistance increases, and steaming weakens.
- Previous: no more
- Next: Steaming rate measurement instrument



 Current
Location:
Current
Location: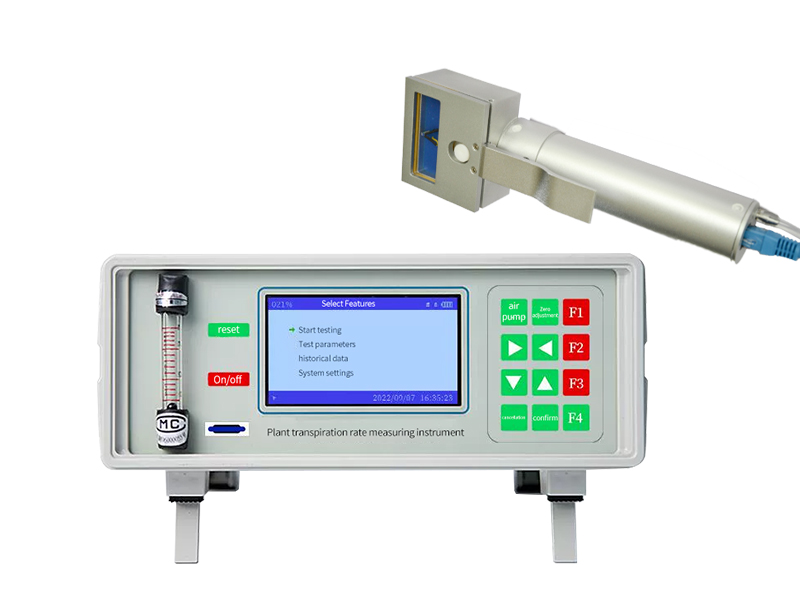
 +86 17853698681
+86 17853698681 WhatsApp
WhatsApp Product Details
Product Details Related Products
Related Products